INTRODUCTION
Toxicokinetic studies are necessary to evaluate the efficacy of mycotoxin detoxifiers, considering the possible effects on the oral absorption and disposition of the mycotoxins in broiler chickens. The detoxification capacity of mycotoxins binder for fumonisin B1 (FB1) is rather limited.
OBJECTIVE
The aim of the present study was to determine the effects of an anti-mycotoxins agent based on minerals, phytogenics and organic components on the plasma concentration-time profile of FB1 in broiler chickens.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
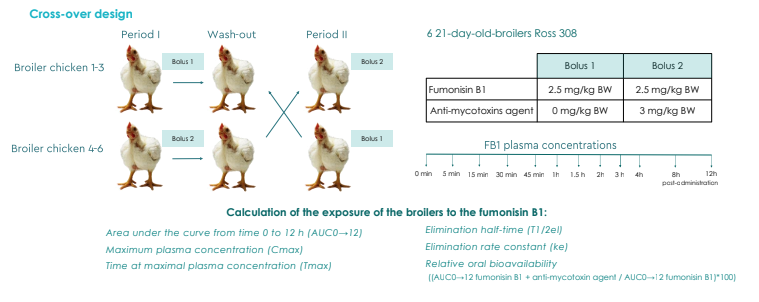
RESULTS
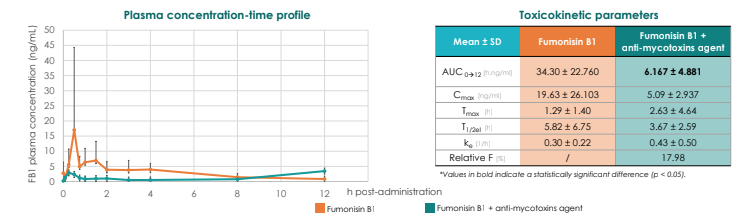
CONCLUSIONS
The anti-mycotoxins agent containing minerals, phytogenics and organic components reduced the oral absorption of fumonisin B1, being efficient in reducing the total systemic exposure to fumonisin B1 in broiler chickens.




