INTRODUCTION
Oxidative stress is an important mechanism of deoxynivalenol (DON) toxicity. DON mycotoxin generates free radicals that
disrupt the redox balance and induce DNA damage and apoptosis in the liver.
In this context, natural plant extracts have received a great deal of attention due to their powerful antioxidant capacity,
among a wide range of beneficial-health properties.
OBJECTIVE
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the in vitro capacity of an anti mycotoxins agent that contains a combination of polyphenolic compounds from turmeric (curcumin) and milk thistle (silymarin) extracts to reduce the oxidative stress induced in hepatic cells by DON.
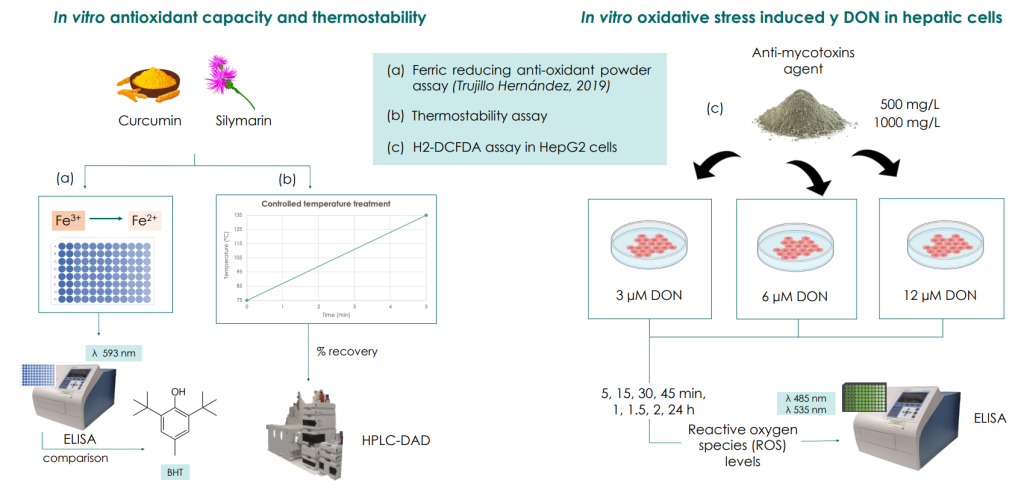
MATERIALS AND METHODS
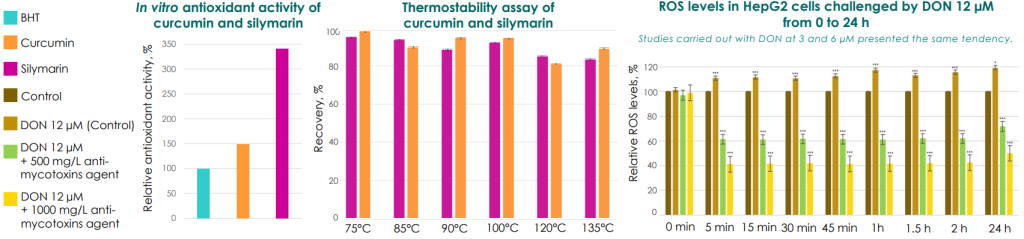
RESULTS
CONCLUSIONS
The combination of curcumin and silymarin is a thermostable combination of natural extracts that provide effective antioxidant activity to alleviate the oxidative stress induced by DON in hepatic cells