INTRODUCTION
Toxicokinetic studies based on absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of mycotoxins, are crucial for the evaluation of the efficacy of mycotoxin detoxifiers in swine. The ineffective detoxification and excretion of aflatoxins in swine, causes them to become particularly sensitive to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) exposure (Popescu et al., 2022).
OBJECTIVE
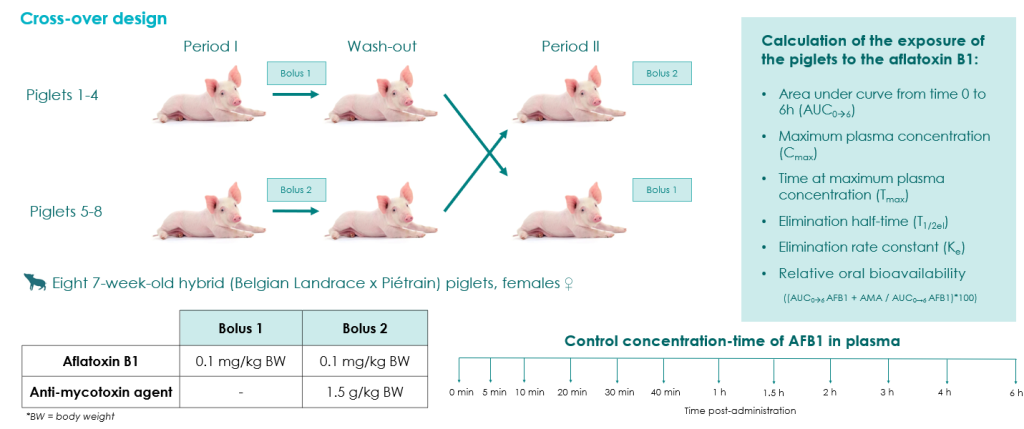
The aim of the present study was to determine the effectiveness of an anti-mycotoxin agent (AMA) based on minerals, phytogenics and yeast products on the reduction of the oral bioavailability of AFB1 by measuring the plasma concentration-time profile of AFB1 in piglets.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
CONCLUSIONS
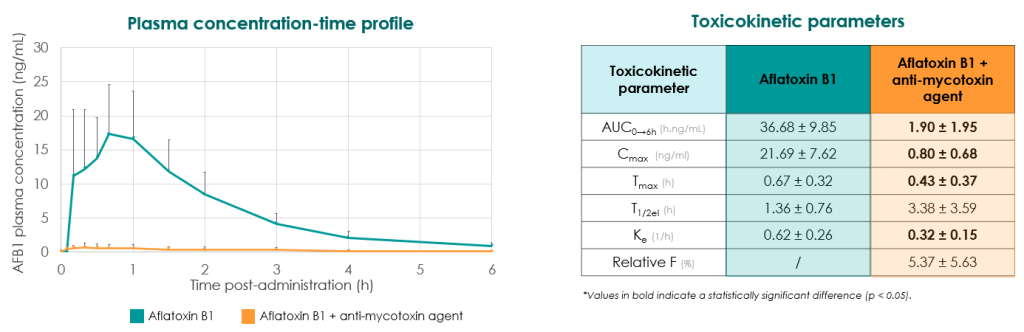
The anti-mycotoxins agent containing minerals adsorbents, natural phytogenics and yeast products, is highly efficient in reducing total systematic exposure to aflatoxin B1 in pigs.